https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14502
14502번: 연구소
인체에 치명적인 바이러스를 연구하던 연구소에서 바이러스가 유출되었다. 다행히 바이러스는 아직 퍼지지 않았고, 바이러스의 확산을 막기 위해서 연구소에 벽을 세우려고 한다. 연구소는 크
www.acmicpc.net


내 답안
import sys import copy from collections import deque input = sys.stdin.readline N, M = map(int, input().split()) lab = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(N)] dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0] dy = [0, 0, -1, 1] def find_spaces(lab): empty_spaces = [] for i in range(len(lab)): for j in range(len(lab[i])): if lab[i][j] == 0: empty_spaces.append((i, j)) return empty_spaces def bfs(): queue = deque() temp_lab = copy.deepcopy(lab) for i in range(N): for j in range(M): if temp_lab[i][j] == 2: queue.append((i, j)) while queue: x, y = queue.popleft() for i in range(4): nx = x + dx[i] ny = y + dy[i] # 범위를 벗어나면 무시 if nx < 0 or ny < 0 or nx >= N or ny >= M: continue # 0인 경우 바이러스 퍼트림 if temp_lab[nx][ny] == 0: temp_lab[nx][ny] = 2 queue.append((nx, ny)) cnt = 0 for i in range(N): cnt += temp_lab[i].count(0) return cnt empty_spaces = find_spaces(lab) result = 0 for i in range(len(empty_spaces)): for j in range(i + 1, len(empty_spaces)): for k in range(j + 1, len(empty_spaces)): a, b, c = [empty_spaces[i], empty_spaces[j], empty_spaces[k]] lab[a[0]][a[1]], lab[b[0]][b[1]], lab[c[0]][c[1]] = 1, 1, 1 cnt = bfs() result = max(result, cnt) lab[a[0]][a[1]], lab[b[0]][b[1]], lab[c[0]][c[1]] = 0, 0, 0 print(result)
Review
문제를 보고 생각했던 논리는 아래와 같습니다.
1. 벽을 세울 수 있는 곳의 개수를 센다.
2. 벽을 3개씩 세우는 모든 경우(brute force)를 BFS(너비 우선 탐색)를 돌립니다.
3. 그 중 가장 큰 값을 결과로 내놓습니다.
for i in range(len(empty_spaces)): for j in range(i + 1, len(empty_spaces)): for k in range(j + 1, len(empty_spaces)): a, b, c = [empty_spaces[i], empty_spaces[j], empty_spaces[k]] lab[a[0]][a[1]], lab[b[0]][b[1]], lab[c[0]][c[1]] = 1, 1, 1 cnt = bfs() result = max(result, cnt) lab[a[0]][a[1]], lab[b[0]][b[1]], lab[c[0]][c[1]] = 0, 0, 0
i, j, k로 3개의 벽을 세울 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 표현하였습니다.
lab[a[0]][a[1]], lab[b[0]][b[1]], lab[c[0]][c[1]] = 1, 1, 1벽을 세우고,
cnt = bfs() result = max(result, cnt)
탐색 후 안전 영역의 개수를 세고,
lab[a[0]][a[1]], lab[b[0]][b[1]], lab[c[0]][c[1]] = 0, 0, 0다시 연구실을 초기화해줍니다.
또한 바이러스가 침투한 영역을 원래대로 돌려놓기 위해
bfs 함수가 작동할 때, deepcopy()를 사용해서 연구실에 바이러스가 침투하기 전으로 초기화를 시켜줄 수 있습니다.
본격적으로 예제 입력 2에서 어떻게 작용하는지 그림으로 알아볼게요.
find_spaces(lab)
함수를 통해서, 0이 존재하는 2차원 배열의 인덱스를 뽑아 줄 수 있어요.
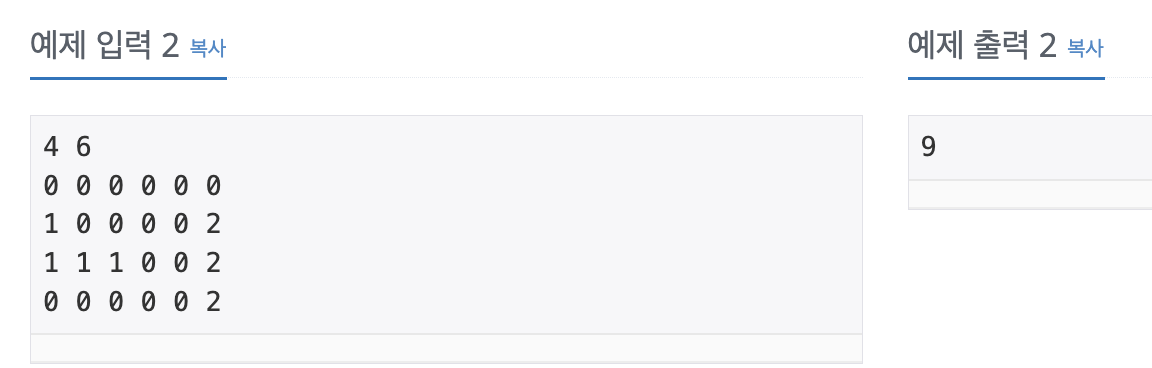
예제 입력 2 에서는 벽을 세울 수 있는 전체 조합은
[(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (0, 3), (0, 4), (0, 5), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4),
(2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 0), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4)]
입니다.
여기서 3개의 조합으로 하기 위해 3중 for문을 사용하였습니다.
덱(deque) 자료구조는 바이러스 위치부터 탐색을 하게 됩니다.



처음에 모든 경우를 알 필요가 있나?라고 생각하여 알고리즘을 짜다가 막혀서
결국 모든 경우를 탐색해 보는 코드로 구현하였습니다.
다른 풀이 방법이 있다면 댓글로 공유 부탁드립니다.
( ̳• ·̫ • ̳)
질문이나 지적할 사항 있으면 언제든지 의견 주세요
( •́ .̫ •̀ )
'BOJ > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스] 해시 파이썬 (4) | 2024.03.23 |
|---|---|
| 백준 7568번 덩치 파이썬 (0) | 2024.03.22 |
| 백준 14719번 빗물 파이썬 (0) | 2024.03.19 |
| 백준 1966번 프린터 큐 파이썬 (0) | 2024.03.08 |
| [프로그래머스] 의상 파이썬 (1) | 2024.02.12 |